Selective Soldering: A Need for Innovation and Development
Improving nozzle wettability will permit more challenging joints to be tackled.
by Samuel J. McMaster, Andrew Cobley, John E. Graves and Nigel Monk
Selective soldering utilizes a nozzle to apply solder to components on the underside of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This nozzle can be moved to either perform dips (depositing solder to a single component) or draws (applying solder to several components in a single movement). The selective soldering methodology thereby permits the process to be tailored to specific joints and permits multiple nozzle types to be used if required on the circuit board.
Nozzles can vary by size (internal diameter) and shape (making them suitable for different process types). This is all dictated by board design and process requirements. Selection of the nozzle type depends on the product to be soldered and the desired cycle time. Examples of different nozzle types are shown at pillarhouse.co.uk.
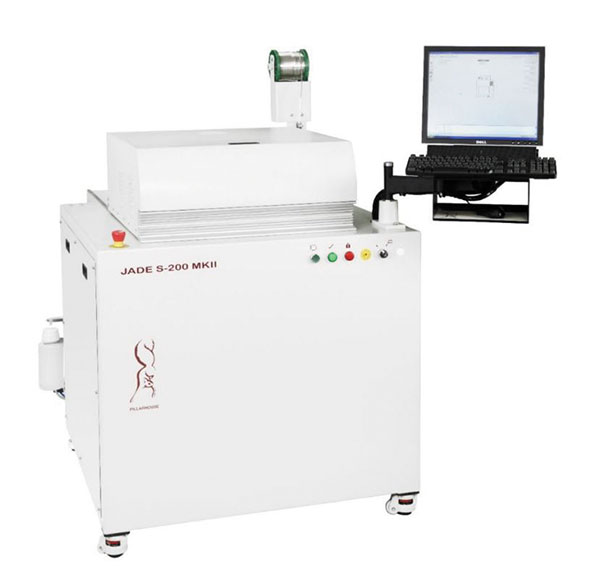
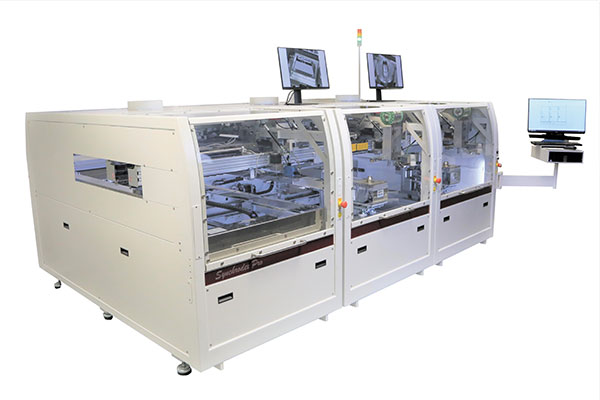
Hand-load selective systems must be programmed with the parameters for multiple solder joints. Many inline systems are designed to be modular, however. This modularity permits multiple solder stations with different conditions/nozzles to achieve low cycle times. FIGURE 1 shows the two distinct types of selective soldering systems offered by Pillarhouse International Ltd.


Selective soldering provides many other benefits compared to wave and hand soldering, such as:
- Minimal thermal shock
- Lower running costs than wave soldering
- Operation under an inert environment to minimize soldering defects, reduce dross production and improve wetting performance (more details below)
- Applicability to low- and high-volume production
- Repeatability in the process and solder joints
- Fewer operators required.
Key attributes of nozzles. To ensure controlled application of the solder is maintained throughout the process, the solder must wet (adhere) to the nozzle. Wettability is the study of the adhesion of liquids to solids because of the interaction between the surface energy of the solid and the surface tension of the liquid. Surface energy (known as surface tension when referring to liquids) is a result of the relative bond strength of the material and the level of unbalanced forces at the surface. Multiple methods exist to characterize surface energy, depending on the components of the surface interaction that can be measured; however, the most common is measuring the contact angle of a stationary (sessile) droplet.
When no other forces act upon a liquid droplet (i.e., no contact with other surfaces and no air resistance due to movement), it will form a sphere as its own surface tension pulls it into that shape, as it is the minimum energy shape it can be. When in contact with a solid, the droplet will deform and spread. The amount of spreading and the angle of the interface between the liquid and solid is a product of the relation between the surface tension of the liquid and the surface energy of the solid. FIGURE 2 demonstrates scenarios with various levels of wetting. When the surface energy of the solid is greater than the surface tension of the liquid, the droplet will spread more and have a lower contact angle. Figure 2a and 2b are examples of this.
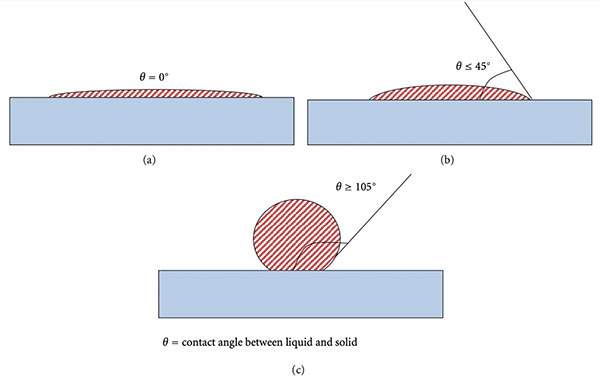
Typically, a static system would be preferred for wettability studies, but we are dealing with a dynamic process in the case of a nozzle. In this instance, the wetting of the solder to the tip of the nozzle maintains a stable radial wave and achieves control during the soldering process by maintaining a stable dome shape to deposit solder.
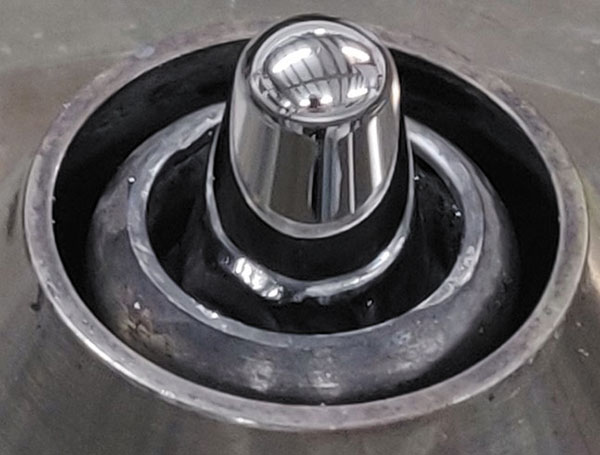
FIGURE 3 shows a well-wetted nozzle in which the solder is adhered to the entire outer surface of the nozzle and therefore has a stable radial wave. This permits good control during the selective soldering process. The static wettability for this nozzle would be akin to Figure 2a or 2b.

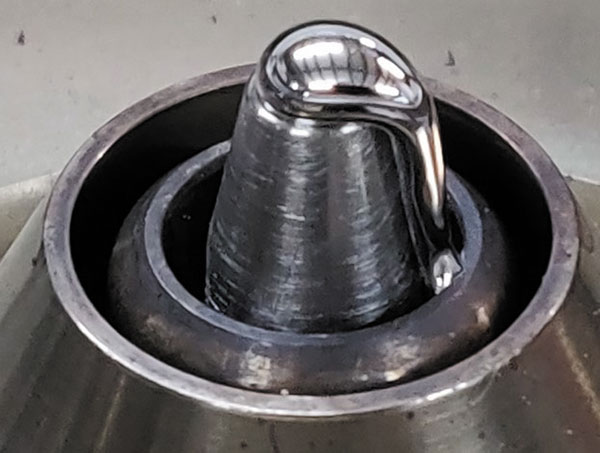
In the case of a material to which solder does not readily wet (non-wetting), the surface energy of the nozzle (or other material being wetted) is not enough to overcome the surface energy of the solder and therefore the solder will maintain a single stream, as shown in FIGURE 4. The static wettability of this nozzle would produce a large contact angle such as in Figure 2c.

Wetting between the liquid solder and nozzle requires a clean interface with minimal surface oxides on the nozzle. The presence of oxides on the surface interferes with wetting of the solder to the surface by acting as a barrier; additionally, the surface energy of oxides is too low for wetting to occur. Flux is used to remove oxides and generate/maintain this clean interface before and during operation. After cleaning, a chemical reaction between the solder and nozzle determines the extent of the wetting, but this interaction also limits the lifetime of the nozzle. It causes nozzle wear, and metal is leached into the solder bath. Exposure to the solder and the subsequent reaction alone does not cause significant wear. The contribution of liquid flow increases wear in a synergistic effect which suggests that the underlying mechanism is complex corrosion-erosion.
Therefore, a good nozzle must have good wettability to solder, ensuring that control can be maintained during the selective soldering process, in addition to a balance between the corrosion and wetting. The materials composition must be chosen carefully to achieve this. For example, extremely wettable materials such as copper have a high dissolution rate and will therefore be completely leached into the bath within hours, demonstrating the link between the wear process and wetting.
The need for development. Currently, the selective soldering industry sees innovation with the production of new machines, pump types and nozzle cleaning. The study of materials for nozzles has seen only minor development, however. A new nozzle material will reduce operation and maintenance costs for manufacturers by reducing the number of nozzles required overall and reducing downtime caused by nozzle failure. Improving the wettability of nozzles will permit more challenging joints to be tackled using the selective method. The current nozzles have a lifetime of approximately 200 hrs. (smaller nozzles wear faster, however, as they are smaller). This project has been undertaken in response to customer requests to increase nozzle lifetime and reduce maintenance.
Other players in the selective soldering industry have developed new nozzles with similar structures based on commonly applied electroless nickel-immersion gold coatings, but this approach uses materials already known to work in the industry. It is well known that the electronics industry is conservative in many regards and rightly so: “Why fix what isn’t broken,” especially when reliability is paramount? There has been a distinct lack of research in nozzle development. Each selective soldering manufacturer is highly secretive surrounding the materials used for their nozzles but there has been some noted development in nitriding as a surface engineering technique to extend the lifespan of wave soldering apparatus.
This groundbreaking research project is partly funded by Innovate UK and Pillarhouse International Ltd., in partnership with Coventry University through a knowledge transfer partnership scheme. The aim is to develop a new, longer-lasting nozzle with excellent wetting properties. By applying the studies of tribology and materials science, fundamental work looking at different materials and surface engineering techniques has selected a number of potential candidates that show improved performance.
Prototype testing has been used to confirm compatibility with existing solders and fluxes. The new AP Master Nozzle will be available in June 2023. 
Samuel J. McMaster is materials scientist KTP associate, Andrew Cobley is professor and theme lead, and John E. Graves is associate professor at the Functional Materials and Chemistry Research Group, Research Centre for Manufacturing and Materials, Institute of Clean Growth and Future Mobility at Coventry University; s.mcmaster@pillarhouse.co.uk. Nigel Monk is managing director at Pillarhouse International (pillarhouse.co.uk).
This special advertising content is sponsored by Pillarhouse International Ltd.


